Population Density by Country a Complete Guide
Explore our guide to population density by country. We break down what the numbers mean, the factors that shape them, and their impact on our world.

Ever heard that Mongolia has more horses than people? That little tidbit is a great, real-world way to start thinking about population density. At its core, it's just a measure of how many people live within a certain space, usually one square kilometer.
This simple number tells a vivid story. It's the difference between a place like Macau, where over 21,000 people cram into each square kilometer, and a vast, open country like Mongolia, where you'll only find about 2 people in that same amount of space. This single metric gives us a powerful snapshot of a nation's geography and the daily life of its people.
What Is Population Density

Think about it like this: imagine a sold-out concert with thousands of fans packed shoulder-to-shoulder. Now, picture that same group of people spread out across a massive national park. The number of people hasn't changed, but their experience and how they interact with their surroundings are completely different. That's the essence of population density.
The formula is dead simple: Total Population ÷ Land Area. But the story it tells is anything but. It’s not just about how populous a country is, but how its people are spread across the landscape. A high density doesn't necessarily mean a place feels "overcrowded," just that its inhabitants live in closer proximity. A low density, on the other hand, points to wide-open spaces between towns and cities.
Why This Metric Matters
For anyone interested in geography—or even strategy games that model the real world—population density is a critical piece of the puzzle. It shapes everything from a country's architecture and infrastructure to its economy and environment.
Here are just a few things it directly influences:
- Infrastructure: Densely populated regions need massive public transit systems, high-rise buildings, and hyper-efficient utilities to function.
- Economic Activity: Big cities with high densities are almost always economic powerhouses, concentrating jobs, innovation, and commerce.
- Resource Management: The challenge of providing water, food, and power gets a lot more complicated when more people share the same square kilometer.
- Social Dynamics: How people commute, socialize, and live their daily lives is fundamentally shaped by how much space they have.
Population density is more than a statistic; it's a narrative about how geography, history, and economics converge to shape human settlement. It explains why one nation builds upwards into the sky while another builds outwards across plains.
This metric helps us make smarter comparisons. For instance, China and Canada are both enormous countries, but looking at their population densities reveals two completely different ways of life dictated by mountains, plains, and climate.
A Quick Global Snapshot
To really wrap your head around this, just look at the extremes. The differences across the globe are staggering. You'll often see tiny city-states topping the charts while huge nations with inhospitable climates sit at the very bottom. It’s a clear illustration of how much physical geography directs where we choose to live.
The following table gives you a high-level summary of these extremes. It really drives home the vast differences between the world's most crowded corners and its most open frontiers.
Global Population Density at a Glance
This table provides a high-level summary of population density extremes, highlighting the vast differences between the world's most crowded places and its most open spaces.
| Category | Example Country/Territory | Approx. People per sq km | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Highest Density | Macau | ~21,946 | Extreme density often occurs in small, highly urbanized city-states. |
| High-Density Nation | Bangladesh | ~1,350 | Fertile land and historical factors can create high density in larger nations. |
| Low-Density Nation | Mongolia | ~2 | Vast, challenging terrain like deserts and steppes leads to sparse settlement. |
| Lowest Density | Greenland | ~0.03 | Massive ice sheets make the vast majority of the land uninhabitable. |
Looking at these numbers, you can almost feel the difference—from the constant energy of Macau to the profound solitude of Greenland's icy expanse. This contrast is what makes population density such a fascinating lens for viewing the world.
How Population Density Is Really Calculated
On the surface, calculating population density seems simple enough. Just take a country's total population and divide it by its total land area, right? Well, that gives you a number, but it rarely tells the whole story of how people actually live.
Think about Canada. The standard formula gives it a population density of about 4 people per square kilometer. But this calculation lumps in millions of square kilometers of frozen Arctic tundra where almost nobody lives. It completely misses the fact that most Canadians are clustered in cities right along the U.S. border.
To get a real feel for how crowded or sparse a place is, you have to dig a little deeper than that first, simple number.
Refining the Calculation
The basic method I just described is called arithmetic density, and it's the most common one you'll see. It’s a useful starting point, but it can be really misleading for countries with huge swathes of uninhabitable land.
To paint a more accurate picture, geographers and demographers use a few other tools:
- Physiological Density: This one is fascinating. It divides the total population by the amount of arable land—the land that can actually be used for farming. This tells you how much pressure a population is putting on its food supply.
- Agricultural Density: This metric zooms in even further, comparing the number of farmers to that same area of arable land. It gives you a great snapshot of how efficient a country's farming sector is.
A country like Egypt is the perfect example. Its arithmetic density is quite low because of all that desert. But its physiological density is through the roof, since nearly everyone lives and farms along the narrow, fertile strip of the Nile River Valley.
Where Does the Data Come From?
These numbers don't just appear out of thin air. They're the product of massive, ongoing data collection efforts that form the bedrock of how we understand our world.
The two main pillars of this data are:
- National Censuses: These are the gold standard. Governments conduct official counts of their entire population at regular intervals.
- UN and World Bank Estimates: For the years between censuses, or for countries where data is hard to come by, international organizations like these create sophisticated models and projections.
This population data is then combined with geographic area measurements—which can also vary. Some calculations might exclude massive inland lakes, while others include them. That's why you sometimes see slightly different density figures for the same country depending on the source.
The real art of understanding population density lies in knowing which questions to ask about the data. Is it including vast deserts? Is it accounting for massive mountain ranges? The answers reveal the true story of human settlement.
Modern tools are making these calculations more precise than ever. To get a better handle on the technology that powers this kind of spatial analysis, check out our guide on what are geographic information systems.
Why Context Is Everything
Getting these nuances right is a huge deal, especially for things like urban planning and resource management.
For instance, the Philippines has a density of around 392 people per square kilometer, which creates enormous challenges for infrastructure, housing, and services. Contrast that with Norway, where a density of just 15 people per square kilometer allows for a completely different approach to everything from environmental protection to city design.
You can see more of these striking global comparisons over at Visual Capitalist, where they show how urbanization shapes population density. It’s a powerful reminder that the number itself is just the beginning—understanding the geography behind it is what truly brings the picture to life.
A Look at the Most Densely Populated Places

When you scan a list of the world's most densely populated countries, a fascinating pattern jumps out. The top spots aren't held by massive nations like China or India, but by tiny city-states, micro-nations, and small island territories.
These are places where unique geography and powerful economies have created an incredible concentration of human life. Instead of just rattling off numbers, let's explore the stories behind these bustling hubs. They're living laboratories for urban innovation, showing what happens when a lot of people have to share a very small space.
The City-State Superstars
At the absolute peak of population density, you'll find places that are essentially entire countries packed into a single city. Monaco, Singapore, and Vatican City are the classic examples. Their small land area and magnetic economies create a gravitational pull for people and capital.
- Monaco: This glamorous speck on the French Riviera crams nearly 19,000 people into just two square kilometers. It's a haven for the wealthy, thanks to its tax laws and luxurious lifestyle, resulting in a stunning landscape of high-rises clinging to steep hillsides over the Mediterranean.
- Singapore: A true marvel of urban planning, Singapore supports over 8,000 people per square kilometer. Faced with extreme land scarcity, the nation has become a world leader in vertical farming, hyper-efficient water recycling, and a public transit system that other cities can only dream of.
These city-states prove that high density doesn't have to mean chaos. Through meticulous planning and forward-thinking policies, they’ve managed to create some of the most livable and prosperous places on the planet.
This trend of extreme density in small territories is perfectly illustrated by Macau. As a Special Administrative Region of China, it holds the title of the most densely populated territory in the world, with around 21,946 people per square kilometer. Its status as a global gambling and tourism hub drives this incredible concentration. You can dive deeper into the numbers by checking out the most densely populated countries in 2025 on aviationa2z.com.
The Pressures and Payoffs of Proximity
Of course, living shoulder-to-shoulder comes with immense challenges. The constant pressure on housing, infrastructure, and green space is a daily reality. Real estate prices are often astronomical, and finding a quiet moment can feel like a genuine luxury.
But the benefits are just as powerful. High density fuels incredible economic dynamism. When you gather that much talent, capital, and creativity in one place, innovation happens. This proximity also supports a vibrant cultural scene, where world-class dining, art, and entertainment are just a short walk or train ride away.
Living in a high-density environment is a constant trade-off. You might sacrifice personal space, but in return, you gain unparalleled access to opportunity, culture, and human connection. It's the engine that powers the world's most dynamic cities.
Seeing these population clusters on a map offers a powerful perspective on how geography shapes human settlement. If you're interested in making your own data-driven visuals, you can learn how to create custom maps to better understand these patterns yourself.
Ultimately, studying the world’s most crowded corners gives us a fascinating glimpse into the future of urban living. As more of the world's population flocks to cities, the lessons learned in places like Macau, Monaco, and Singapore become more relevant for everyone. They are pioneering the solutions that will help cities everywhere become more sustainable, efficient, and livable for generations to come.
Exploring the World's Emptiest Countries

We've just walked through the packed city streets of the world’s most crowded places. Now, let’s take a journey to the opposite extreme: the planet’s most wide-open spaces.
If high-density nations are a sold-out concert, these countries are a private park stretching all the way to the horizon. Out here, the main challenge isn't navigating crowds—it's conquering sheer distance. In these vast territories, nature still calls the shots.
The Geography of Emptiness
Countries like Mongolia, Namibia, and Australia are a masterclass in how geography dictates human settlement. Their incredibly low population densities aren't an accident. They're a direct consequence of landscapes that are as beautiful as they are unforgiving.
- Mongolia: Known as the "Land of the Blue Sky," it’s a nation defined by immense, grassy steppes and the Gobi Desert. With a density of just 2 people per square kilometer, it stands as the most sparsely populated sovereign country on Earth. Its famous nomadic culture is a brilliant adaptation to this environment.
- Namibia: Dominated by the Namib and Kalahari deserts, Namibia is one of the driest countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Its stunning but arid landscapes can only support about 3 people per square kilometer.
- Australia: It's a continent-sized country, but most of its population famously lives clustered along the coasts. The enormous, dry Outback makes up the vast majority of its landmass, pushing the overall density down to just 3.4 people per square kilometer.
These places reveal a simple truth: where it's hard to farm, build, or find water, people are few and far between. The land itself sets a natural speed limit on growth.
Life in the Wide-Open Spaces
Living in a low-density country comes with a unique set of challenges—the mirror opposite of life in a place like Monaco. For starters, building and maintaining infrastructure across huge distances is a monumental and costly task.
Just imagine laying down a highway or a power grid that has to cross hundreds of kilometers of empty desert simply to connect two small towns. This is the reality. For governments in these nations, ensuring remote communities get reliable access to healthcare, schools, and even decent internet is a constant logistical puzzle.
In sparsely populated countries, distance is the ultimate currency. The time and resources required to connect people, deliver goods, and provide services define the rhythm of daily life and shape national policy.
This fosters a powerful sense of self-reliance and community. Your neighbors might be kilometers away, but you often depend on each other in ways a city-dweller might find hard to imagine.
Comparing High vs. Low Population Density Countries
To really get a feel for how population density shapes a nation, a side-by-side comparison is the best way to see the differences in action. It’s amazing how this single metric influences everything from the economy to the architecture.
The table below contrasts two countries from opposite ends of the spectrum, highlighting how their realities are worlds apart.
| Feature | High-Density Example (e.g., Singapore) | Low-Density Example (e.g., Mongolia) |
|---|---|---|
| Geography | Small island city-state, intensely urbanized. | Vast steppes, mountains, and desert landscapes. |
| Economy | A global hub for finance, trade, and technology. | Focused on mining, agriculture, and livestock herding. |
| Urbanization | 100% urban; a city of high-rises and vertical living. | Roughly 69% urban; life is centered on the capital. |
| Main Challenge | Managing land scarcity and high housing costs. | Developing infrastructure and delivering services over vast areas. |
What this shows is that neither high nor low density is inherently "better" or "worse." Each presents a unique set of problems to solve and advantages to build upon, making the study of population density a fascinating window into human ingenuity.
The Key Factors That Shape Population Density
Population density numbers tell us the "what" and "where" of human settlement, but the real story is in the "why." No country's population map is an accident. It’s the result of powerful, interconnected forces that have guided where people build their lives for thousands of years.
Think of it as a complex puzzle where geography, money, and history are the main pieces. How they fit together determines whether a nation’s map shows tight clusters of humanity or vast, empty spaces. Once you understand these core drivers, you can look at any country and start to piece together the story behind its numbers.
This visual below breaks down the primary forces that influence where people live.
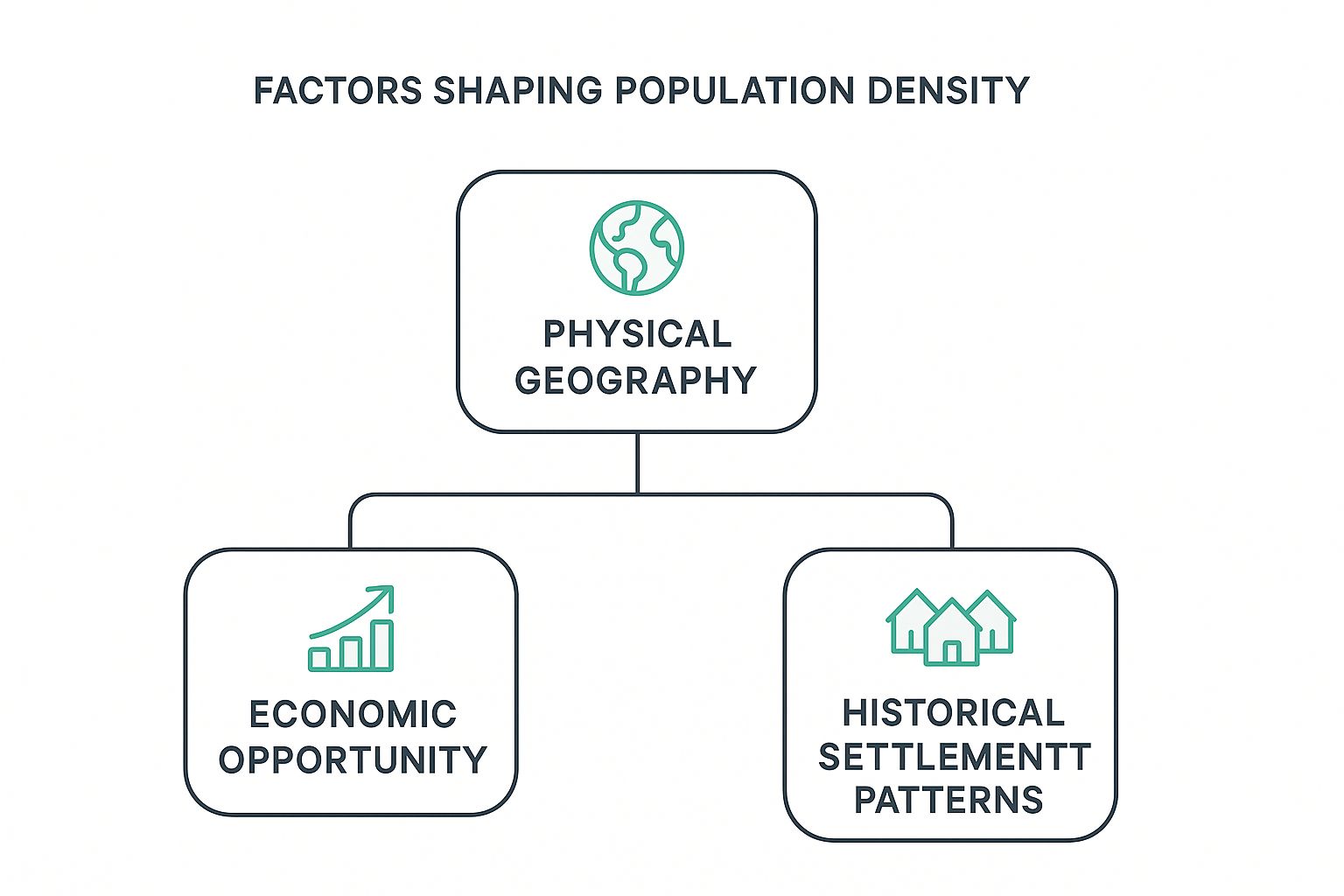
As the diagram shows, the physical landscape often lays the foundation. That, in turn, influences where money and opportunity flow, shaping settlement patterns over the long haul.
The Power of Physical Geography
Before anything else, the land itself sets the rules. Humans have always been drawn to places where they can not just survive, but thrive. Certain geographic features have always acted like magnets for settlement.
- Access to Water: Civilizations are born on the banks of rivers and the shores of oceans. Water provides transportation, supports farming, and makes trade possible. Just look at Egypt, where over 95% of the population lives in the narrow, fertile Nile Valley—a tiny green ribbon in a vast desert.
- Climate and Terrain: Extreme environments—scorching deserts, frozen tundras, and towering mountain ranges—naturally push people away. It’s no surprise that Canada’s population is overwhelmingly clustered along its southern border, far from the harsh Arctic north.
- Fertile Land: Historically, the single most important factor was arable land. You can't build a society without food. Regions with rich soil, like the Ganges Plain in India, can support massive agricultural populations, leading to high densities that persist for centuries.
These geographical building blocks help explain why some areas are packed and others are nearly empty. To see how climate and terrain define these living spaces on a global scale, check out our guide to the different biomes of the world.
Economic Opportunity and Urbanization
While geography may have drawn the original lines on the map, economic forces are constantly redrawing them. In the modern world, the single strongest magnet for population is opportunity. People follow the jobs, and this relentless migration has fueled the explosive growth of cities everywhere.
You can see this clearly in coastal clustering. Brazil is a fantastic example. The country has a massive interior, but its population is crammed into coastal megacities like Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. Why? Because that’s where the economic action is.
A country's economic landscape acts like a gravitational field, pulling people toward centers of commerce and innovation. The denser these economic hubs become, the stronger their pull, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of urbanization and growth.
This global stampede toward city life is a primary reason we see pockets of extreme density, even inside countries that are otherwise sparsely populated.
Historical Settlement and Policy
Finally, the past has a long shadow. Where people live today is often a direct echo of historical events, ancient trade routes, and centuries-old settlement patterns. Europe’s dense network of cities, for example, still largely follows the blueprint laid down during the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages.
Government policy also plays a huge role. A government might offer incentives to settle a remote region or, like Brazil did with Brasília, build a new capital from scratch to intentionally shift its population inland. On the flip side, a lack of investment in rural infrastructure can leave vast areas with very few people.
These enduring patterns, created over generations, are a story written on the land itself, shaped by geography, wealth, and the decisions of those who came before us.
How Density Data Gives You an Edge in Geography Games
Embedded content
For anyone who loves geography games, understanding population density is more than just trivia—it's a secret weapon. When you're dropped into a random spot in a game like GeoGuessr or Worldle, the visual clues related to density can be the key to clinching a high score.
Think of it as landscape detective work. The density of housing, the style of farming, and the way a city is laid out are all massive hints. A sprawling, low-rise suburb with wide, empty roads just screams North America, while a jumble of narrow streets and compact, ancient buildings is a dead giveaway for a historic European city.
Once you start recognizing these patterns, the game changes. You're no longer just guessing; you're making smart deductions based on how people have organized their lives in that specific space.
Reading the Environmental Clues
Every scene in a geography game is packed with information. The trick is knowing what to look for and connecting it back to the number of people living per square kilometer.
Here are a few practical tips to get you started:
- Architecture Tells a Story: Are the buildings tall, multi-story structures packed tightly together? You’re likely looking at a high-density hub like Hong Kong or Singapore. On the other hand, single-family homes with big yards are a classic sign of lower-density countries like Australia or Canada.
- Infrastructure is a Giveaway: Check out the roads and public transit. A complex web of train lines, subways, and bus routes is a hallmark of a major city that needs to move millions of people around efficiently.
- Farmland Holds Clues: Do you see enormous, industrial-sized fields worked by massive machines? That's typical in sparsely populated agricultural giants. In contrast, small, terraced farms carved into hillsides tell a story of a place where every inch of usable land is precious, like in parts of Southeast Asia.
This screenshot from a game shows a classic rural scene, but the details tell you everything you need to know about its density.
The vast, open fields and sparse trees, paired with a simple two-lane road, immediately help you rule out the densely populated regions of Europe or Asia. It points directly toward a more sparsely settled part of the world.
By mastering these visual cues, you’re not just playing a game—you’re applying real-world geographic principles. Population density becomes a practical tool that turns subtle environmental details into decisive points on the leaderboard. It’s the ultimate edge for any digital explorer.
A Few Lingering Questions About Population Density
As we've journeyed from packed city-states to wide-open plains, a few questions tend to pop up again and again. Let's tackle them head-on to clear up some of the most common points of confusion.
Population Density vs. Overpopulation
It’s tempting to use these terms as synonyms, but they describe two totally different concepts.
Population density is just the math. It’s a neutral measurement telling you how many people live within a set area, like a square kilometer. Think of it as a simple fact, like the temperature in a room.
Overpopulation, on the other hand, is a value judgment. It’s the idea that an area’s population is too large for its resources—like water, food, or infrastructure—to support. A sparse region can be overpopulated if it lacks basic resources, while a jam-packed city might be thriving if it's well-managed.
Here’s a simple analogy: Density tells you how many people are in the elevator. Overpopulation describes the feeling when there isn’t enough air for everyone inside.
Which Country Has the Highest Population Density?
This one needs a little precision. If you’re only looking at fully sovereign nations, the tiny Principality of Monaco takes the top spot. It crams an incredible 19,000 people into every square kilometer, a result of its immense wealth and tiny footprint on the French Riviera.
But if we expand the list to include dependent territories, Macau blows everyone else away. This special administrative region of China packs in nearly 22,000 people per square kilometer, a density driven by its unique economy and extremely limited land. The distinction is a great reminder of why definitions matter when you're comparing stats.
How Does Population Density Affect Real Life?
So, how does this number actually change the way people live? The impact is massive and touches almost every part of society.
- Traffic and Commutes: In high-density places, you absolutely need complex public transport to avoid total gridlock. Daily commutes are often longer and definitely more crowded.
- Housing Costs: When lots of people compete for a small amount of space, real estate prices skyrocket. This is why you see smaller apartments and a lot more skyscrapers in dense cities.
- Public Spaces: Urban parks and city squares become precious "green lungs" in concrete jungles. In contrast, low-density areas have all the natural space you could want, but might lack those central, shared community hubs.
At the end of the day, population density shapes everything from the price of your coffee to the design of the building you call home.
Ready to turn your geographic knowledge into a fun adventure? Join EarthChasers and explore the world's most fascinating places, from dense cities to remote wilderness. Start your global journey at https://earthchasers.com.
